A fructooligosaccharide (also written fructo-oligosaccharide) is a carbohydrate, which is made out of a short chain of fructose molecules. It is also classed as an oligosaccharide; oligo meaning few and saccharide, sugar. Fructooligosaccharides are also sometimes called oligofructose. Often the term is abbreviated to the letters FOS.
Together with inulin fiber, fructooligosaccharides are probably most recognized for their prebiotic qualities.
They are very similar but not identical to inulin: the difference being in their chemical structures. Fructo-oligosaccharide chains of molecules are shorter than inulin chains.
Where Can I Find FOS?
You can find FOS in certain natural foods including:
- Bananas
- Onions
- Tomatoes
- Chicory
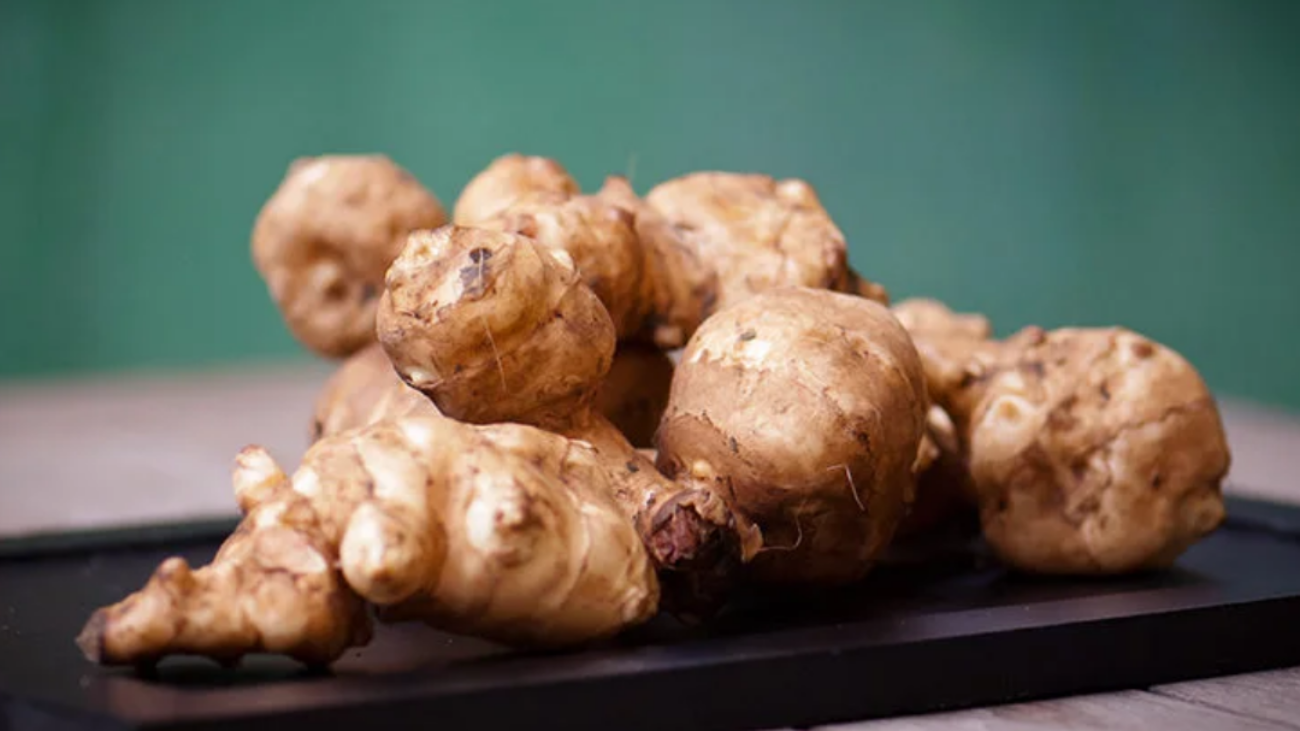
- Sunchokes or Jerusalem artichokes
- Yacón
- Barley
- Wheat
Of these foods the sunchoke or Jerusalem artichoke and its relative, the yacón have the highest concentrations of FOS.
You will also find that fructo-oligosaccharide or oligofructose, as it is also known, is added to many processed foods, mainly as a prebiotic or fiber supplement but also as a sweetener.
This type of FOS is not natural. Most is manufactured using a chemical process, in which fungal enzymes are added to white sugar (sucrose), acting upon it and turning it into FOS. Some fructooligosaccharides are also made by the hydrolysis (breaking down) of inulin from chicory. FOS is becoming increasingly popular as a prebiotic and is now added to many types of processed foods in the US. You may already have come across this additive in the foods you buy. As a prebiotic, FOS is very similar in terms of properties to inulin. It can be considered beneficial to your health as it:
- Is virtually undigested by the human digestive system so arrives in the colon unaltered, providing a food source forbeneficial bacteria
- Has low calorific value.
- Increases the population of bifidobacteria in the colon.1,2
- Acts as a non-digestible fiber in the diet and so can help relieve constipation.
Additionally FOS has been shown to:
- Enhance magnesium absorption.3
- Promote calcium absorption.4
Like inulin fiber, FOS appears to be a good thing. Before you decide to try it though, you should be aware of its side-effects.
What Are the Side Effects of Taking a Fructooligosaccharide?
Before you decide that fructooligosaccharides are for you, you should be aware that they:
- Have been shown in some scientific studies to increase the growth of “bad” bacteria such as Klebsiella Pneumonia and other less-friendly organisms such as E. Coli and many Clostridium species5,6. Klebsiella Pneumonia is associated with the auto-immune disease Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and also worryingly is becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics both in the US and elsewhere.
- Are likely to cause an increase in gas, abdominal discomfort and bloating if taken in large quantities.
Should I Take Fructooligosaccharides?
It is clear then that FOS has both advantages and disadvantages. Should you take it and if so how should you take it?
Given that fructooligosaccharides appear to be able to feed less friendly organisms in the colon, we think it is prudent to avoid high quantities of FOS if your digestive flora is very unbalanced.
Large amounts of FOS are usually found in supplements such as probiotics, stand-alone fructooligosaccharide supplements or processed foods. Natural foods contain small amounts of fructo-oligosaccharides in a less concentrated form and, depending on your situation, you may be able to manage these lesser amounts.
Gut dysbiosis, intestinal candida and food intolerance symptoms are sure signs that you have a gut flora imbalance, so if this is you, be sure to avoid foods and supplements with added FOS. If you are in this situation and are taking a
probiotic supplement to help you re-balance your digestive flora, be sure to choose one which is free from FOS and other prebiotics. Also if you have Ankylosing Spondylitis then high quantities of fructooligosaccharides are not for you.
If you are free of these ailments then FOS may be of help to you. Have a word with your physician before you begin and remember to start with small quantities only and ramp up slowly!
Where Can I Buy Fructooligosaccharides (FOS)?
You can buy FOS in supplement form as a stand-alone product or combined with probiotics.
Internet retailer iHerb.com also supplies a fantastic range of stand-alone FOS supplements as well as probiotics containing FOS. Their international shipping rates are also very reasonable. Click here to browse their store and receive $5 USD off your first purchase.








 Dr Ohhira has shown that this strain of bacteria inhibits the MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) superbug, Escherichia coli 0157 (E. Coli 0157) as well as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), which causes peptic ulcers. He has also demonstrated that Enterococcus faecalis TH10 is 6.25 times stronger than other naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria.
Dr Ohhira has shown that this strain of bacteria inhibits the MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) superbug, Escherichia coli 0157 (E. Coli 0157) as well as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), which causes peptic ulcers. He has also demonstrated that Enterococcus faecalis TH10 is 6.25 times stronger than other naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria.



